Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)#
Introduction#
The Global Biotic Interactions is an open-access platform that focuses on indexing and providing access to data about biotic interactions. These interactions can range from predation, parasitism, mutualism, to various other ecological relationships between organisms.
GloBI aggregates data from various sources, including scientific literature, field observations, and existing datasets, and stores this information into a unified format. This standardized data enables researchers, ecologists, and anyone interested in biodiversity to access and analyze data about biotic interactions more easily.
GloBI continuously scans existing data infrastructures and registries and tracks the biotic interactions data they make available. Found biotic interaction data are then resolved and integrated. So, rather than being a giant centralized repository of biotic interaction data, GloBI is more of a search index that helps to find existing biotic interaction datasets in their native cyber-habitat. For more information about how GloBI works, please visit the Data Integration Process page.
There are many different forms to have a dataset indexed by GloBI, however, in this guide we will cover the method which covers the FAIRification process described in this guide.
Creating a GitHub repository#
There are many different forms to make GloBI index a dataset as described in GloBI contribute page. Here we will cover the this process using a GitHub repository, but other methods can also be used with adaptations.
Warning
You need a GitHub account to create repositories. Go to Signup page and create an account if you do not have one yet.
Log in into the GitHub platform using your account credentials.
Create a new GitHub repository by cloning the GloBI template repository
Give a name to the repository. The repository will be created at your account namespace (Owner).
Choose if you want to make your repository public or private. Private repositories are not accessible by others and can not be indexed by GloBI. You can choose to initially create a private repository and when you are ready you can make it public.
Click the
Create repositorybutton.Upload the biotic interactions data file in text-delimited format (e.g. CSV, TSV) to the repository (
Add file->Upload files)
Creating a metadata using EML#
While GloBI does not require a metadata description using EML (Ecological Metadata Language) for data publication, adhering to FAIR principles necessitates the provision of access to metadata through the EML standard.
EML documentation can be generated using the ezeml tool as described below:
First create a new account in ezeml
Create a new EML document and add all information for the minimum set of terms for biotic interactions datasets (optionally also include the RECOMMENDED terms to improve reusability of datasets) described in the Metadata standardization.
Fill the description of
data tableandcolumns mapping(see Documenting data and column mapping).Export the EML file using the menu:
Import/Export->Download EML file (XML).Save the EML (XML) file locally.
Documenting data and column mapping#
In order to GloBI read and process the dataset the EML (XML) file must include the description of the data table. In the ezeml tool this can be created using the Data Tables menu (Fig. 4). Change the field Online Distribution URL to point to file with biotic interactions data in the GitHub repository.
Note
The direct URL of a file can be generate from GitHub using the Raw button in the file preview page (Fig. 3)
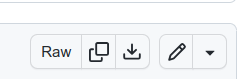
Fig. 3 Generate direct URL for a file in GitHub by clicking in the Raw button.#
The original data table with biotic interaction records must be uploaded using CSV file and then the columns mapping can be created using GloBI vocabulary as attribute name. First you need to load a text-delimited file into ezml (Fig. 4). After successful upload the file, the original columns can be mapped to GloBI vocabulary and Darwin Core standard.
To edit the columns mapping click on Edit Column Properties button in the Data Table page (Fig. 4).
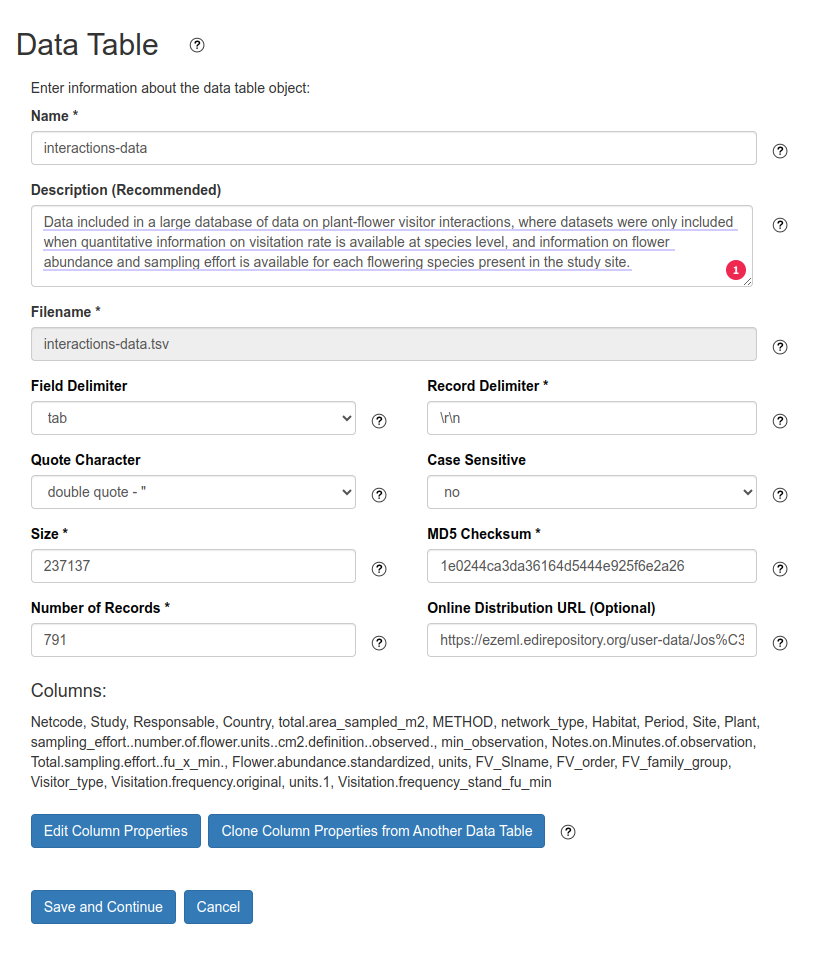
Fig. 4 Loading a data table in ezeml tool.#
In the Columns Properties page, select the column which you want to map and click on the Edit Properties button (Fig. 5).
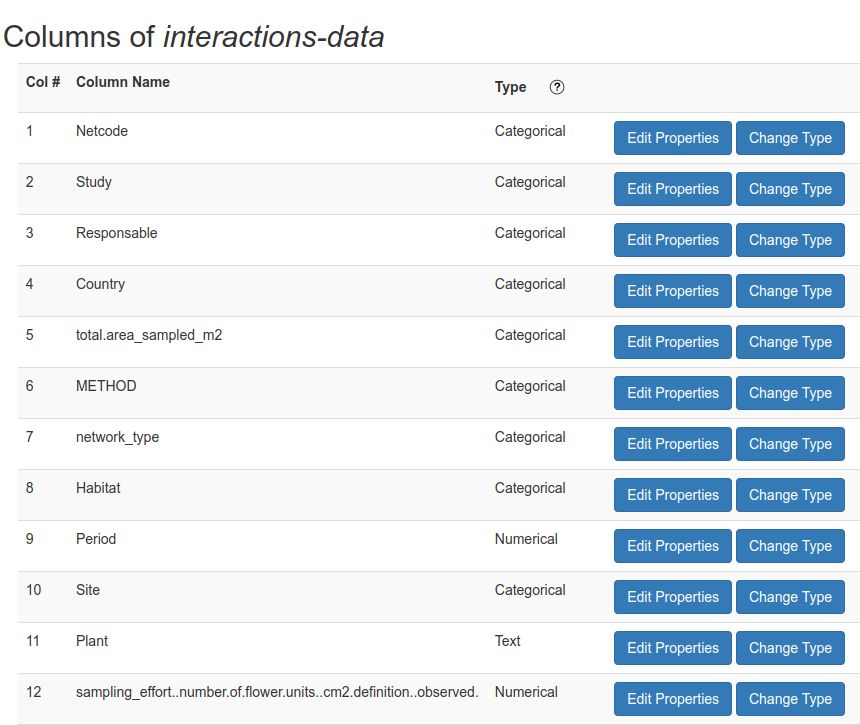
Fig. 5 Columns Properties page in ezeml tool. To edit the mapping of a specific column click on Edit Properties button.#
In the column properties page you MUST fill the fields: Name and Definition as following (Fig. 6):
Namewith a term from theGloBI vocabularyif available. You may use terms from other standards or vocabularies whenGloBI vocabularylacks a term, or alternatively, you can provided your own definition for the columnDefinitionwith the URL (ID) of the term in the DwC standard or any other standard/ontology in order to provide a machine readable definition for the column
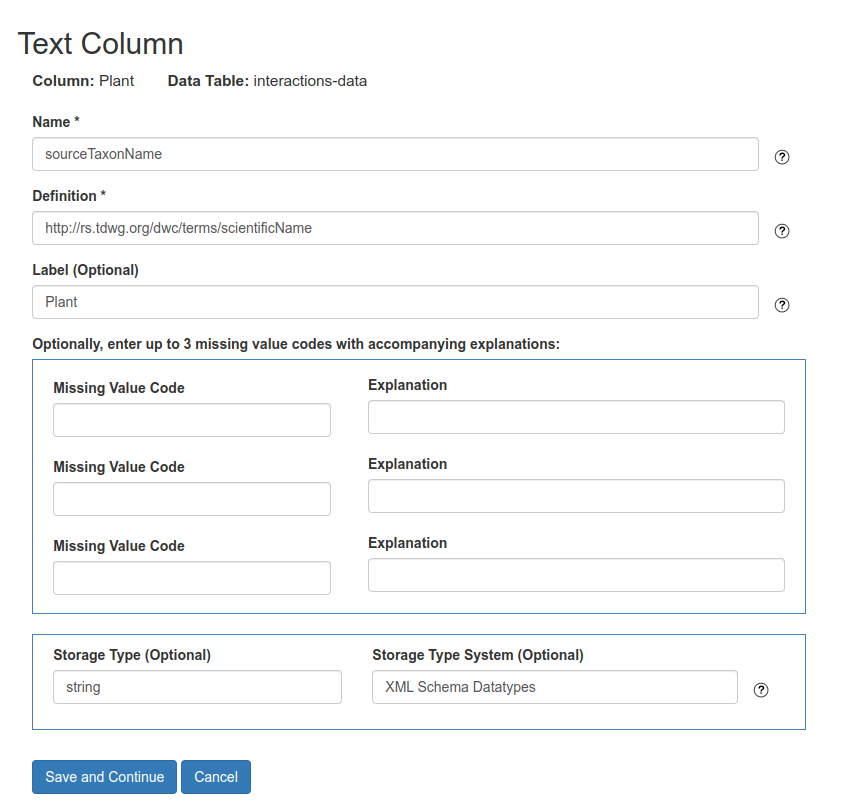
Fig. 6 Column mapping to GloBI vocabulary and Darwin Core standard. The fields Name and Definition MUST be provided.#
When all columns have been mapped to GloBI vocabulary or to DwC and PPI, continue with metadata description, exporting the EML (XML) file at the end.
Preparing the GitHub repository for GloBI#
The new created repository will look like shown in Fig. 7.
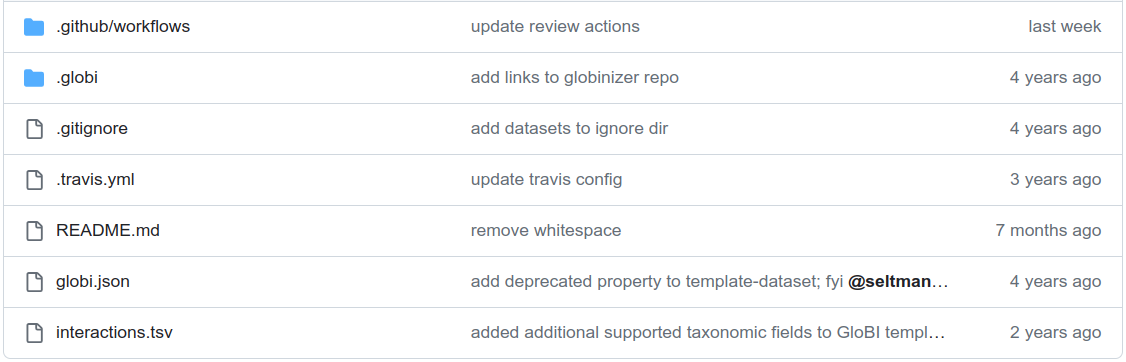
Fig. 7 File structure of a new created GitHub repository from GloBI’s template#
There are four files that you need to edit/create to enable GloBI to find and index your data:
README.md: a markdown file where you can freely describe your dataset in human readable form.interactions.tsv: the biotic interactions records in TSV file format. You can choose to delete this file and use another text format file (e.g. CSV, TXT).globi.json: this file guides GloBI in how to find, read and process the (meta)data of your dataset, but since we are using the EML to describe the dataset this file can be renamed toglobi.json.disabled. Renaming the file will still enable GloBI to find the repository but it will use theeml.xmlfile instead of theglobi.jsonto process the interaction data.eml.xml: upload the EML (XML) file created using the ezml tool to the repository. NOTE: make sure that theeml.xmlfile includes theData Tabledescription, otherwise GloBI will not be able to process the dataset (see Documenting data and column mapping).
Persistent Identifier#
GloBI provided PUID using Content Hash Identifiers for all datasets published in the platform. For example the SHA256 hash hash://sha256/20cc192510e0abb7c982a50502354fa74d504cfa serves as a PID for the datasets hosted at globalbioticinteractions/carvalheiro2023.
Alteratively, GloBI can generate DOI by uploading a copy of the dataset from GitHub into Zenodo. To create a PID from GitHub you MUST create a release of your repository (Fig. 8), after creating a release the generated data package will be uploaded to Zenodo and a DOI will be also generated.
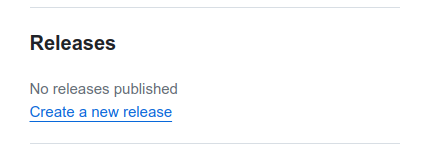
Fig. 8 Generate a release from GitHub repository in order to get a DOI from Zenodo.#
